Call Custom Functions
When developing a plugin, there are two components to consider: the frontend and the backend.
In this guide, we'll cover how to create a custom endpoint in a backend plugin, and call it from a frontend plugin.
INFO
For additional documentation on the differences between a frontend and backend plugin - click here.
Registering an Endpoint
Let's start by creating an endpoint called multiply in our backend plugin.
multiply will take two numbers, output the result in the backend logs, as well as return the result. This endpoint will used by the frontend later on.
/packages/backend/src/index.ts
import { SDK, DefineAPI } from "caido:plugin";
function multiply(sdk: SDK, a: number, b: number) {
const result = a * b;
sdk.console.log(`The product of the multiply call is: ${result}`);
return result;
}
export type API = DefineAPI<{
multiply: typeof multiply;
}>;
export function init(sdk: SDK<API>) {
sdk.api.register("multiply", multiply);
}Script Breakdown
First, the necessary type aliases are imported. SDK is the interface used to interact with Caido. DefineAPI is used to structure the API: definining what methods or endpoints are available, the parameters those methods accept and what types of values they return.
import { SDK, DefineAPI } from "caido:plugin";Next, the function is defined. The function takes three parameters: sdk, a and b. The sdk parameter is typed using the SDK alias to give the function access to its utilities. The a and b parameters are expected to be numbers as this function multiplies the two together.
function multiply(sdk: SDK, a: number, b: number) {
const result = a * b;
sdk.console.log(`The product of the multiply call is: ${result}`);
return result;
}Using the DefineAPI utility, we are stating what our API offers. In this case, the multiply function is available to be called. To ensure the function receives the expected parameter data types, typeof is used to link the multiply API call to the multiply function definition. This definition is stored in the type alias API and exported so it can be used in other files.
export type API = DefineAPI<{
multiply: typeof multiply;
}>;Next, we define a function that will run as soon as Caido loads the plugin. It extends upon the base SDK by adding the <API>. In order to register the function, we use the sdk.api.register() method which takes two parameters: a string name for the function and the function it refers to. We give the name "multiply" to the multiply function.
export function init(sdk: SDK<API>) {
sdk.api.register("multiply", multiply);
}Calling the Endpoint
Now that we've created our endpoint in the backend plugin, we can call multiply from our frontend plugin.
/packages/frontend/src/index.ts
import { Classic } from "@caido/primevue";
import PrimeVue from "primevue/config";
import { createApp } from "vue";
import type { Caido } from "@caido/sdk-frontend";
import type { API } from "../../backend/src/index.ts";
import App from "./views/App.vue";
export type CaidoSDK = Caido<API>;
export const init = (sdk: CaidoSDK) => {
const app = createApp(App);
app.provide("sdk", sdk);
app.use(PrimeVue, {
unstyled: true,
pt: Classic,
});
const root = document.createElement("div");
Object.assign(root.style, {
height: "100%",
width: "100%",
});
app.mount(root);
sdk.navigation.addPage("/multiply-page", {
body: root,
});
sdk.sidebar.registerItem("Multiply", "/multiply-page", {
icon: "fas fa-calculator",
});
};/packages/frontend/src/views/App.vue
<script setup lang="ts">
import Button from "primevue/button";
import InputNumber from "primevue/inputnumber";
import { inject, ref } from "vue";
import type { CaidoSDK } from "../index";
const sdk = inject<CaidoSDK>("sdk");
const inputA = ref(0);
const inputB = ref(0);
const result = ref<string>("Result will appear here.");
const calculate = async () => {
if (!sdk) return;
const value = await sdk.backend.multiply(inputA.value, inputB.value);
result.value = `Result: ${value}`;
};
</script>
<template>
<div class="h-full flex flex-col p-4 gap-4">
<div class="flex flex-col gap-2">
<label class="text-sm font-medium">First Number</label>
<InputNumber v-model="inputA" inputClass="w-full" />
</div>
<div class="flex flex-col gap-2">
<label class="text-sm font-medium">Second Number</label>
<InputNumber v-model="inputB" inputClass="w-full" />
</div>
<Button label="Calculate" @click="calculate" />
<p class="text-gray-400">{{ result }}</p>
</div>
</template>Script Breakdown
The frontend setup imports the necessary type aliases and creates a Vue application. The CaidoSDK type alias extends the base Caido type with the API we defined in the backend.
import type { Caido } from "@caido/sdk-frontend";
import type { API } from "../../backend/src/index.ts";
export type CaidoSDK = Caido<API>;The Vue app is created with PrimeVue configured using the Classic preset. The SDK is provided to all components using Vue's dependency injection system.
const app = createApp(App);
app.provide("sdk", sdk);
app.use(PrimeVue, { unstyled: true, pt: Classic });The Vue component uses reactive refs for the input values and result. When the button is clicked, it calls sdk.backend.multiply() with the input values and updates the result display.
TIP
For additional documentation on creating a page - click here.
The Result
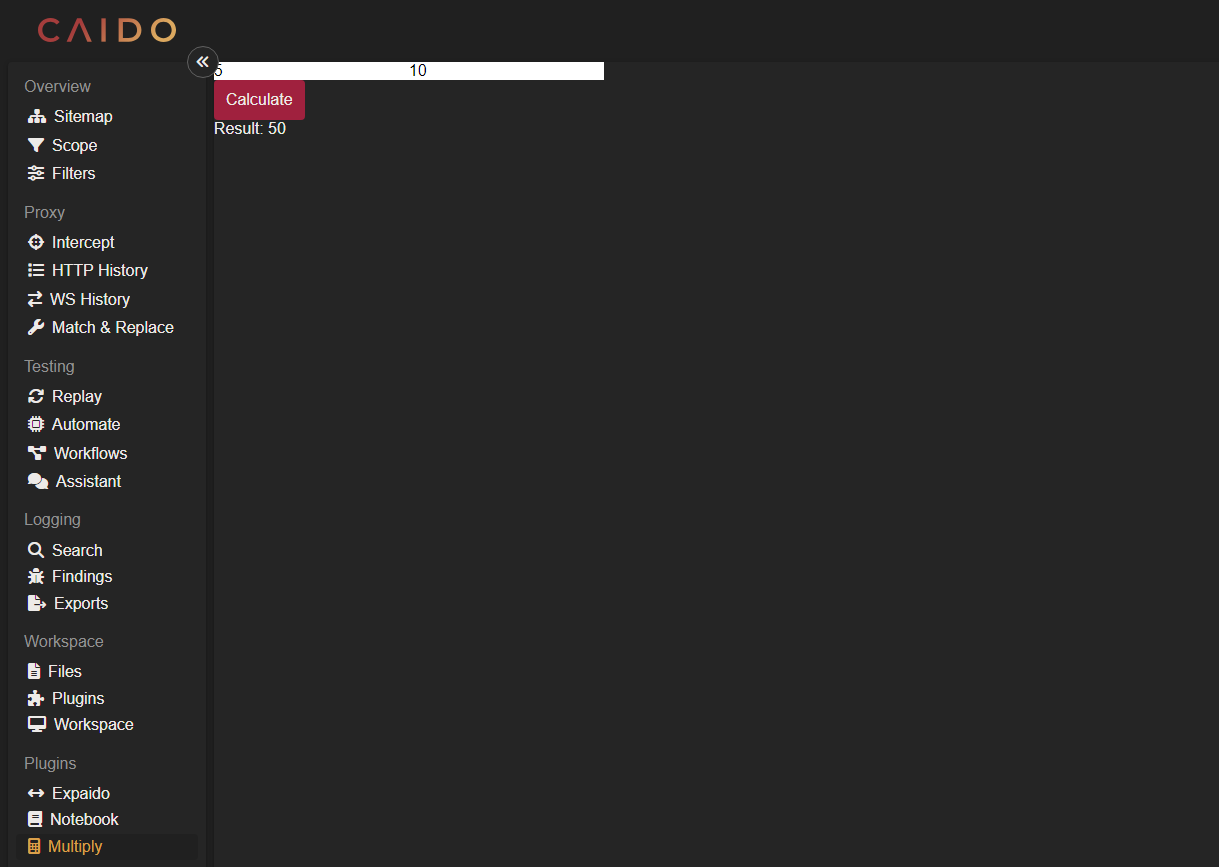
The entry to your Caido log file should resemble:
2024-11-05T13:26:13.528023Z INFO plugin:5a758b74-e176-473f-a545-bdb452015b9a js|sdk: The product of the multiply call is: 15